Si APD-200-LCC
Avalanche photodiodes are used in situations where more sensitivity and lower noise are needed compare to standard PIN detectors. These devices use an internal gain mechanism to generate secondary electrons via impact ionization. This in turn sets off an electron avalanche which amplifies the initial signal for easier measurement. APDs are often used in applications having very low signal levels, such as LiDAR or ranger-finders. 4in1 Photonics offers Si avalanche photodiodes (APDs) with a spectral wavelength range from 400 nm to 1100 nm. These devices provide high operation frequency, high multiplication gain and low noise.
DA0411200LC is a 200µm active diameter Si APD. It designed for high volume, cost-effective commercial distance-meter, range-finder and high-speed laser scanning applications. This APD is available in leadless, ceramic-carrier (LCC) SMD package that comes with clear glass or built-in 635 nm, 650 nm, or 905 nm filter window options.
Features
ü High speed, low noise
ü High gain at low bias voltage
ü Surface mount with filter windows (635nm, 650nm, 905nm, 400-1100nm)
ü RoHS-compliant
Specifications
Ts=25°C
Parameter | Symbol | Minimum | Typical | Maximum | Test Conditions |
Active diameter | D | - | 200μm | - | - |
Spectral response range | λ | 400nm | - | 1100nm | - |
Responsivity | Re | 35A/W | 50A/W | - | λ=800nm, M=100 |
Response time | tr | 0.3ns | 1ns | λ=800nm, RL=50Ω | |
Dark current | ID | 0.05nA | 0.2nA | 1.0nA | M=100 |
Breakdown voltage | VBR | 80V | - | 200V | IR=10μA |
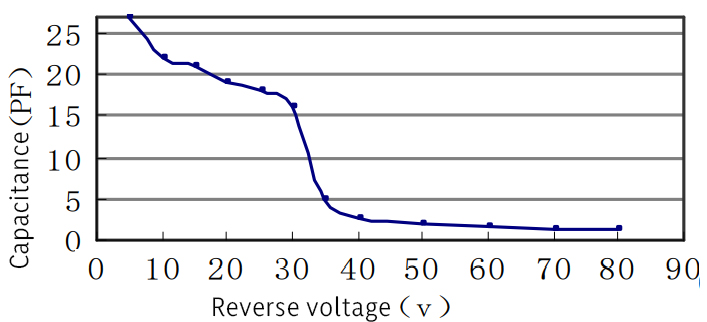
Capacitance | Ct | - | 2 pF | - | M=100 |
Gain | M | - | 60 | 100 | λ=800nm |
VBR Temperature coefficient | Γ | - | 0.6V/ ºC | - | Tc=-40 ºC~+85 ºC |
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter | Symbol | Minimum | Maximum | Test Conditions |
Operating temperature | Top | -45 ºC | 85ºC | No dew condensation |
Storage temperature | Tstg | -45ºC | 100ºC | No dew condensation |
Forward current | IF | - | 1mA | - |
Reverse voltage | VR | - | 190V | - |
Lead soldering time | Tsol | - | 10sec. | 260ºC |
Spectrum response | Capacitance vs. Reverse voltage |
Gain vs. Reverse voltage
| Dark current vs. Reverse voltage
|
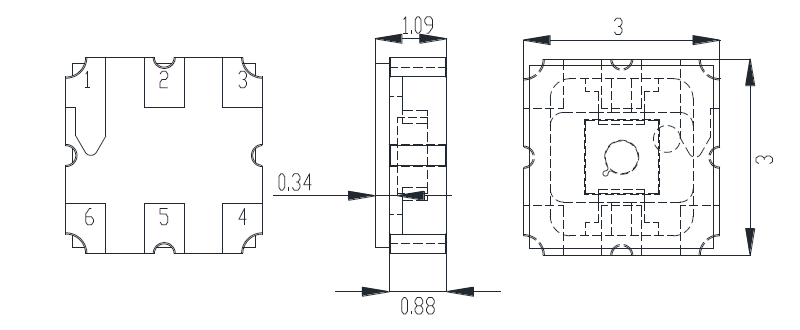
Dimensions
LCC-3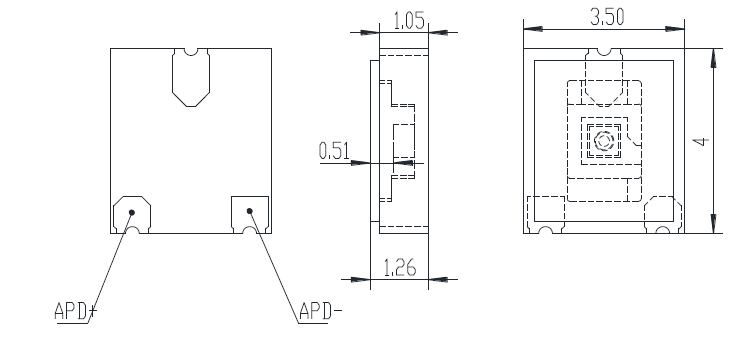
LCC-6